
Google ranks websites based on more than 200 factors. However, not all factors have the same importance. Some factors have a bigger impact on your website's ranking on Google search. This article delves into 50 of the most crucial Google ranking factors that SEO strategists and website owners must consider to improve their site’s visibility.
On-Page SEO Factors
1. Keyword in the Title Tag
Search engines pay attention to the title tag. Its a mini SEO factor. The tag is supposed to accurately depict what's on the page.
Let me elaborate. A title tag is an HTML element that defines the title of a webpage. It's crucial for both SEO and user experience. The title tag usually shows up at the top of a browser's window and acts as the main headline when a webpage is shown on search engine results pages (SERPs).
In HTML, the title tag looks like this:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Your Page Title Goes Here</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>The text in the title tags is what shows up on the browser tab and in the clickable link on search results. It gives you a quick and accurate idea of what's on the webpage.
Search engines use Title Tags to figure out what a page is about. It's better to have relevant, descriptive title tags with keywords to improve your webpage's visibility and ranking on search engines. Also, good title tags can attract users and make them want to click on the link, so it's an important part of on-page optimization strategies.
Using the right words in the title of your webpage, is like giving Google a roadmap to your content. Think of it as a spotlight for your page in the vast world of search results. It's not just about putting any words; it's about picking the ones that people might type when looking for something like what you have.
Now let's discuss the length of the Title Tag. Many SEOs recommend to keep the length of the title tag to 65 characters. Now, here's the catch, Google – John Mueller, when asked about the 65 characters limitation of title tag as a ranking related factor, he said “No. We don’t have any recommendation for the length of a title.”
And here's another thing to note: we cannot repeat the title tag on different pages, so make sure you don't use the same title tag for different pages. When you're setting up your title tag, think about your target keyword – the main word that captures what your page is all about. Nail that, and you're on your way to standing out in the Google crowd!
2. Keyword in Meta Description
Meta descriptions don't directly affect Google's ranking, but they do impact your rank through click-through rates.
The meta description tag gives a quick overview of the webpage content. Like the title tag, the meta description is crucial for search engine optimization (SEO) and can influence a user’s decision to click on a particular search result.
In HTML, looks like this:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="description" content="Your concise and compelling page description goes here.">
<meta name="author" content="Your Name">
<title>Your Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Your page content goes here -->
</body>
</html>
The content attribute in the meta description tag has a quick summary of the webpage. This description often appears right below the clickable Title Tag on search engine results pages (SERPs), providing users with additional context about what they can expect when clicking on the link.
Good meta descriptions can attract users’ attention, encouraging them to click on a specific search result. It's crucial to have unique and engaging meta descriptions for every page on your website to improve SEO and for making a good user experience.
3. Keyword in H1 Tag
H1 tags are like the second title tags that Google really pays attention to.
The H1 tag is the HTML element for the main heading or title of a webpage. It's the main heading on the page, the one that stands out the most.
In HTML, the H1 tag is formatted as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Your Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is Your Main Heading</h1>
<!-- Your page content goes here -->
</body>
</html>
H1 tags are used by web browsers and search engines to make sense of the content hierarchy on a webpage. The H1 tag is vital for both accessibility and SEO. It helps users and search engines figure out what a page is all about.
It's a good idea to use H1 tags for the main title of a page and then use H2, H3, etc. for subheadings and sections within the content. This not only makes the content easier to read but also helps with SEO by showing the importance and connections between different sections on the page.
4. Keyword Frequency or Topical Authority, What to consider!
In SEO, keyword frequency is the count of how often a particular keyword or phrase appears in content, typically measured as a ratio or percentage of the total word count. Keyword frequency is crucial for on-page optimization. But, you have to avoid keyword stuffing because penalizes it.
In other words, optimizing keyword frequency involves finding a balance between incorporating keywords enough to signal relevance to search engines but avoiding overuse, which can lead to keyword stuffing—a practice that may be penalized by search engines.
The formula for keyword frequency is:
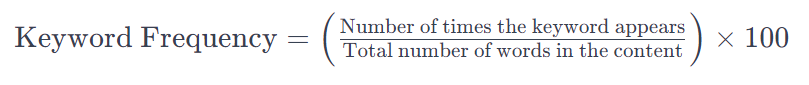
Remember, in modern SEO it's more important to create valuable and natural content for users, rather than obsessing over keyword density. Search engines are super smart these days, they can understand what you're saying and if your content is any good. That's why it's important to take a holistic approach to SEO. You need great content, topical authority and a good user experience.
Topical authority refers to a website's or a page's expertise, credibility, and relevance in a specific subject or topic. It's a concept that search engines use to determine how well a website or page covers a particular subject matter. Establishing topical authority is crucial for improving search engine rankings and attracting organic traffic.
Creating high-quality, comprehensive, and authoritative content on a specific topic is essential. Content should be informative, well-researched, and provide value to the users.
Having a diverse range of content related to a particular topic helps demonstrate expertise. This includes articles, blog posts, videos, infographics, and other relevant formats.
Quality backlinks from reputable websites that are relevant to the topic can boost topical authority. When other authoritative sites link to your content, it signals to search engines that your content is credible.
Metrics such as user engagement, time spent on the page, and low bounce rates indicate that visitors find your content valuable. Positive user signals contribute to topical authority.
Regularly updating and adding new content related to a specific topic shows a commitment to staying current and maintaining topical authority over time.
While the direct impact of social signals on SEO is debated, a strong social presence and sharing of content on social media can indirectly contribute to topical authority.
Using relevant keywords naturally in your content signals to search engines that your content is focused on a specific topic. However, it's crucial to avoid keyword stuffing and prioritize user experience.
Establishing topical authority helps search engines understand that your website is a reliable source of information in a particular niche, increasing the likelihood of ranking well for related queries. It's not just about covering a broad range of topics but demonstrating expertise and depth in the areas that matter to your audience.
5. Content Length
Longer content is preferred over shorter ones.
Content length is all about how many words or characters are in your content, like a webpage, blog post, or article. Content length is a factor search engines consider for evaluating page relevance and content quality.
The length of your content can vary depending on what you want to accomplish with your webpage. Usually, longer stuff is better for certain types of searches, especially if the user query requires a lot of details and information. However, it’s crucial to prioritize quality over the length of the content.
Longer content is helpful, but it needs to be well-written, relevant, and provide value to the user. Just focus on the user intent, what they're looking for and answering their questions.
Content length can vary depending on the type of content. Take product descriptions, for example, they can be brief, while in-depth guides tend to be longer.
Keep the user in mind when deciding how long the content should be. Make sure the content is easy to read, well-organized, and grabs the audience's attention.
Make sure to include relevant keywords in your content, but don’t overdo it. The content should feel natural and give a positive reading experience.
With more people using mobile devices, make sure your content can be seen and read on different screen sizes.
In the end, the aim is to create content that satisfies users, gives valuable info, and matches what your audience expects, instead of just focusing on content length. Google, Yahoo, Bing and other search engines give priority to content that meets user intent and provides a positive user experience.
6. Multimedia
Having images, videos, and all that jazz can indicate the content is quality content.
Awesome images that are relevant to the content can make content more interesting for users. If you want better SEO, make sure to name your image files properly, use descriptive alt text, and compress images for faster loading times.
Adding videos to a website makes it more interesting and keeps users on the page longer i.e. improved dwell time. Search engines love video content, and putting your videos on YouTube can help you get more visibility in search results.
Make your podcasts and audio content more SEO-friendly by adding transcripts, catchy titles, and relevant keywords. It makes audio content easier to find and access.
Visuals and infographics make information easier to understand. Sharing and linking to them increases backlinks and visibility.
Incorporating interactive features like quizzes and surveys can improve dwell time and thus enhance user engagement and SEO.
To win at multimedia in SEO, you gotta optimize all your media elements using descriptive filenames. Make sure to add alt text to images, use relevant keywords, and consider page loading times. User experience is a super important SEO factor.
Multimedia not only makes content more appealing to users but also increases the likelihood of sharing and linking, which can positively influence a website’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs).
7. Keyword Prominence
Having the keyword appear in the first 100 words of the content is a relevancy signal.
In the whole, keyword prominence means how prominently a specific keyword or keyphrase appears on a webpage. It's about how important keywords are in different parts of a page, like headings, titles, and the body text. Keyword prominence is a factor that search engines use to see if a page is relevant to a search query.
Keywords placed in the title tag, especially toward the beginning, are often considered more prominent. The title tag is super important for SEO.
Headings, particularly H1 and H2 tags, play a big role in keyword prominence. Search engines pay attention to keywords in headings.
The target keyword in the opening paragraph emphasizes its importance and relevance to search engines.
Meta descriptions don’t directly affect rankings, but they can help your page stand out for specific search queries.
Including keywords in the URL can boost a page’s visibility. Having a clear and keyword-rich URL structure is good for SEO. But you need to remember that the URLs are not very long. Shorter URLs are better.
Incorporating keywords in image alt text can improve overall keyword prominence, especially for pages with a lot of images.
Don't forget to keep it natural and user-friendly when optimizing for keyword prominence. Like we talked about earlier, stuffing a page with keywords can get you in trouble. Focus on creating high-quality, relevant content that naturally incorporates key terms to enhance SEO performance.
8. Page Loading Speed
Google considers page speed as a ranking factor.
Page loading speed is the time it takes for a webpage to load and show its content. Page speed is crucial for SEO as search engines, especially Google, include it in their ranking algorithms.
Server Response Time is the time for a web server to respond to a browser request.
The size of files, including images, CSS, JavaScript, and other assets. File compression reduces loading times.
Storing website files in a user’s cache improves loading speed for subsequent visits.
When you use a CDN, your website’s content gets distributed across different servers, making load times faster because the server is closer to the user.
Making JavaScript and CSS files smaller and compressed can speed up loading times.
Compressing images can significantly reduce file sizes and improve loading times.
When pages load faster (faster loading times), users are more satisfied and less likely to leave.
Pages that load quickly may receive a boost in the rankings compared to slower pages.
With mobile devices being so popular, page speed is essential for a great mobile experience.
Website owners and developers can check out tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse to see how fast their pages load and where there is a need for improvement. Improving page speed not only benefits SEO but also contributes to a more user-friendly and efficient website.
9. Duplicate Content
Duplicate content can negatively impact a’s search engine visibility.
Duplicate content refers to identical or substantially similar content that appears in more than one location, either on the same website or across different websites. Search engines strive for diverse and relevant search results, but duplicate content presents challenges in displaying the correct version. Resolving duplicate content is crucial for SEO.
Content duplication on various pages of a website, usually unintentional due to CMS settings or site structure.
The website’s “www” and “non-www” versions have identical content. Search engines may treat these as separate entities.
Similar to www and non-www, duplicate content may exist on both HTTP and HTTPS versions of a website.
Republishing the same content across multiple websites without proper attribution.
Search engines might have trouble figuring out which version of content is most relevant, which could result in lower rankings for those pages.
Crawlers have a set amount of resources to go through websites. Duplicate content takes up resources without adding any value.
User Experience: Users might see the same stuff on different pages, which can be confusing and make a poor user experience.
To fix duplicate content problems, webmasters can use canonical tags to show which version of a page is preferred, set up redirects, and keep URLs consistent. Also, using the "rel=canonical" tag and setting your preferred domain in Google Search Console can help with these challenges and boost your SEO performance.
10. Rel=Canonical
If you use this tag correctly, Google won't think your content is duplicated.
The "rel=canonical" tag is an HTML element that lets search engines know the preferred version of a webpage when there are multiple identical versions. This tag is used to fix duplicate content and tell search engines which URL to show in search results.
Here’s how the “rel=canonical” tag is implemented in HTML:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Your Page Title</title>
<link rel="canonical" href="https://www.yourwebsite.com/your-canonical-page">
</head>
<body>
<!-- Your page content goes here -->
</body>
</html>
When you have the same or very similar content on different URLs, you can use the “rel=canonical” tag to indicate the preferred version. This helps search engines decide which version to index and show in search results.
It’s particularly useful in situations where different versions of a page exist, such as HTTP and HTTPS, www and non-www, or mobile and desktop versions. The canonical tag consolidates the signals for ranking purposes.
The canonical tag should be placed in the <head> section of the HTML document. It tells you which URL is best by pointing to the main version of the content.
It’s very useful for e-commerce sites with product variations, paginated content, and syndicated content on different platforms.
Search engines use the canonical tag as a signal, but there's no guarantee they'll strictly follow it. However in practice, search engines usually follow canonical tags and use them to consolidate ranking signals, which improves a website's SEO.
Off-Page SEO Factors
11. Number of Referring Domains
The number of referring domains refers to the total count of unique websites that have at least one external link pointing to a specific domain. Referring domains are an essential metric in backlink analysis and have a significant impact on search engine optimization (SEO) due to several reasons:
A diverse and substantial quantity of referring domains is typically seen as beneficial for SEO. Search engines tend to think a lot of quality backlinks means a site is legit and authoritative.
Search engines value a diverse link profile, meaning that the links to a website come from a variety of sources. A higher number of referring domains contributes to this diversity, making the backlink profile more robust.
Keeping an eye on the number of referring domains can help businesses see how they measure up against other websites in their industry or niche. More high-quality referring domains can give you a leg up.
SEO experts often use tactics to get backlinks from a diverse set of referring domains. This could involve making valuable content, building relationships with other bloggers, or doing outreach for SEO.
With tools like ahrefs, semrush, and ubersuggest, you can find out how many and how good the websites are that link to a specific site.
While the number of referring domains is important, it’s equally crucial to focus on the quality of these domains. Good, trustworthy backlinks are usually better than a bunch of low-quality ones. Search engines check how relevant, authoritative, and trustworthy the referring domains are.
12. Number of Linking Pages
There might be some links from a particular domain to your site; their number is a ranking factor too.
13. Domain Authority
A site’s authority often signifies its trustworthiness, thus affecting its ranking on search engines.
Domain Authority (DA) is a Moz metric that measures how strong a website is. It is a numerical score ranging from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating a greater potential for the domain to rank well in search engine results pages (SERPs). Domain Authority predicts how well a website will rank for certain search terms.
The quality and quantity of backlinks pointing to the domain play a significant role. Having diverse, high-quality links helps improve Domain Authority.
Good content that’s relevant and high-quality helps boost your Domain Authority. You gotta have content that draws in links and keeps users engaged.
A well-organized and user-friendly site structure is important for both users and search engines. It helps improve user experience and boosts Domain Authority.
The effect of social signals on SEO is up for debate, but being active on social media can indirectly boost your Domain Authority, especially if it helps you get more visibility and natural links.
14. Link Relevancy
Link relevancy refers to the degree of connection or similarity between the content of the linking page and the content of the target page that the link is pointing to. In other words, it assesses how relevant the context of the link’s linking to.
Key points about link relevancy:
Search engines consider link relevancy as a valuable signal when determining the authority and value of a backlink. A link from a contextually relevant source is often considered more valuable than a link from an irrelevant source.
The anchor text used in the link can contribute to link relevancy. When the anchor text is closely related to the content of the target page, it provides additional context to search engines.
The overall theme and topic of the linking page and the target page should align to establish link relevancy. For example, a link from a technology-related page to a tech product page is more relevant than a link from an unrelated topic.
Natural link-building efforts often result in links from contextually relevant sources. This happens when other websites naturally link to content because it goes well with or supports the information on their own pages.
Relevance is not only important for search engines but also for users. Links from relevant sources can provide users with additional valuable information and enhance their overall experience.
15. Social Signals
Google considers social signals, such as shares, likes, and comments on social media, as a ranking factor.
Let me elaborate:
Social signals refer to the influence of social media activity on a ’s search engine rankings. These signals indicate how much people are liking and sharing a webpage or website on different social media sites. While the direct impact of social signals on search engine rankings is a topic of debate among SEO professionals, there is evidence to suggest that social media activity can indirectly influence SEO in several ways:
If your content gets a lot of engagement on social media, it is likely to reach a larger audience. If more people can find your website, you'll get more visits, brand exposure, and potential backlinks.
If your content is popular on social media, you might get organic backlinks from other websites, bloggers, or publishers who find and mention your content. These backlinks contribute to a website’s overall authority.
Having a solid social media presence helps build brand authority and trust. Search engines may consider brands with a positive online reputation as more credible.
Search engines may discover new content more quickly if it is shared and discussed on social media platforms. This faster indexing can lead to quicker inclusion in search engine results.
Social signals might kinda impact user engagement metrics, like click-through rates, time spent on site, and bounce rates. If engagement metrics are good, search engines know the webpage is valuable.
Common social signals include likes, shares, comments, and overall social media activity related to a website or its content. It’s important to note that while social signals are considered by some as part of a holistic SEO strategy, search engines like Google have stated that they do not use social signals directly as ranking factors.
Technical SEO Factors
16. Mobile-Friendly Website
Google's mobile-first indexing means they prioritize the mobile version of your site for ranking.
A mobile-friendly website is a site that's made to work well on mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. SEO is all about being mobile-friendly now because everyone uses their phones to browse the internet.
A responsive design ensures that the layout and content of the website adjust dynamically based on the screen size and resolution of the device being used. This prevents the need for users to zoom in or scroll horizontally.
Mobile users often have limited bandwidth and slower internet connections. A mobile-friendly website is optimized for quick loading times to provide a smooth and efficient browsing experience.
Text, images, and interactive elements are appropriately sized and spaced for mobile screens. Navigation menus are designed to be easily accessible and user-friendly on smaller screens.
Buttons, links, and interactive elements are designed to be easily tappable with fingers, considering the touch interface of mobile devices.
Flash-based content is not supported on many mobile devices. Mobile-friendly websites use HTML5 and other mobile-friendly technologies to ensure compatibility.
The viewport meta tag is utilized to control the width and scaling of the viewport, ensuring that the website content fits the screen properly.
Google primarily uses the mobile version of a webpage for indexing and ranking. A mobile-friendly website is more likely to be ranked higher in mobile search results.
Providing a positive user experience on mobile devices contributes to lower bounce rates, increased engagement, and higher conversion rates. Google considers user experience as a ranking factor.
Google has explicitly stated that mobile-friendliness is a ranking factor in its algorithms. Websites that are not mobile-friendly may experience lower rankings in mobile search results.
To determine if a website is mobile-friendly, you can use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test or check for the “Mobile-Friendly” label in Google search results. Ensuring mobile-friendliness is a fundamental aspect of modern SEO practices.
17. Secure Site (HTTPS)
Google announced that HTTPS is a ranking factor, ensuring secure exchanges of information.
A secure site refers to a website that uses the HTTPS protocol to encrypt data transmitted between the user's browser and the web server. The "S" in HTTPS stands for "Secure," and it is an extension of the standard HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) used for communication on the World Wide Web.
HTTPS employs SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or its successor, TLS (Transport Layer Security), to encrypt data exchanged between the user's browser and the web server. This encryption enhances the security and privacy of user information, such as login credentials and personal details.
HTTPS provides authentication, ensuring that users are connected to the legitimate and intended website. This helps prevent man-in-the-middle attacks and phishing attempts.
Secure sites are often perceived as more trustworthy by users. Websites with HTTPS are indicated by a padlock icon in the browser's address bar, instilling confidence in visitors.
Google considers HTTPS as a ranking factor in its algorithms. Secure websites may receive a slight ranking boost compared to their non-secure counterparts. Google has encouraged webmasters to migrate their websites to HTTPS to promote a more secure online environment.
Modern browsers, such as Google Chrome, display warnings for non-secure websites, alerting users that their connection is not secure. This can negatively impact user trust and engagement.
Websites handling sensitive information, particularly those involved in e-commerce and online transactions, must use HTTPS to ensure the secure transmission of payment details.
To implement HTTPS, website owners need to obtain an SSL/TLS certificate from a certificate authority (CA) and install it on their web server. Many hosting providers offer free or paid SSL certificates as part of their services.
18. XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is a file that lists all the important pages of a website to help search engines understand its structure and content. The XML sitemap is created specifically for search engines and is not designed for human visitors. It serves as a roadmap for search engine crawlers, providing information about the organization of the site's content, the priority of pages, and the frequency of updates.
XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a standard markup language that defines rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. The XML sitemap is written in XML format.
The XML sitemap includes a list of URLs (Uniform Resource Locators) for all significant pages on a website. This can include pages, posts, images, videos, and other types of content.
Alongside each URL, the XML sitemap may include additional information such as the priority of the page (relative to other pages on the site) and the frequency with which the page is likely to change.
Search engine crawlers use XML sitemaps to discover and index content on a website more efficiently. This is particularly useful for large websites, new websites, or websites with complex structures.
Webmasters can submit XML sitemaps to search engines, such as Google Search Console, Bing Webmaster Tools, and others. This helps search engines understand the structure of the website and ensures that all important pages are crawled and indexed.
Here is a simple example of an XML sitemap:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9">
<url>
<loc>https://www.example.com/page1</loc>
<lastmod>2023-01-15</lastmod>
<changefreq>weekly</changefreq>
<priority>0.8</priority>
</url>
<url>
<loc>https://www.example.com/page2</loc>
<lastmod>2023-01-20</lastmod>
<changefreq>monthly</changefreq>
<priority>0.6</priority>
</url>
<!-- Add more URLs as needed -->
</urlset>
Webmasters can generate XML sitemaps using various tools or plugins available for popular Content Management Systems (CMS) like WordPress. Regularly updating and submitting an XML sitemap is considered good SEO practice to ensure that search engines are aware of all relevant content on a website.
19. Schema Markup
Schema markup can help Google understand the context of your content.
Schema markup, also known as structured data markup, is a code added to a website's HTML to provide search engines with more detailed information about the content on a page. This structured data helps search engines understand the context and meaning of the content, enabling them to present richer and more informative search results, known as rich snippets or rich results.
Schema.org is a collaborative project supported by major search engines, including Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Yandex. It provides a standardized vocabulary for marking up various types of content on the web.
By implementing schema markup, webmasters can enhance how their content appears in search engine results pages (SERPs). This may include additional information such as ratings, reviews, prices, event details, and more.
Rich snippets are the enhanced search results that display additional information beyond the typical title, URL, and meta description. Schema markup enables the creation of these rich snippets, making search results more engaging and informative.
Schema markup supports a wide range of content types, including articles, events, local businesses, products, recipes, reviews, and more. Each content type has its own set of properties and attributes.
Schema markup is added to the HTML of a webpage using specific tags and attributes. The most common format is in JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data), though it can also be implemented in microdata or RDFa formats.
Example of JSON-LD schema markup for an article:
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"mainEntityOfPage": {
"@type": "WebPage",
"@id": "https://www.example.com/article-page"
},
"headline": "Example Article Headline",
"image": "https://www.example.com/images/article-image.jpg",
"datePublished": "2023-02-01",
"dateModified": "2023-02-05",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "John Doe"
},
"publisher": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Example News",
"logo": {
"@type": "ImageObject",
"url": "https://www.example.com/images/logo.jpg"
}
},
"description": "This is an example article about JSON-LD schema markup.",
"articleBody": "The main text of the article goes here. It can include multiple paragraphs and sections."
}
</script>
While schema markup itself is not a direct ranking factor, it can indirectly impact SEO by improving the visibility and click-through rates of search results. Rich snippets make search results more appealing to users, potentially leading to higher engagement.
Implementing schema markup requires a basic understanding of HTML and the specific schema vocabulary relevant to the content on a webpage. Webmasters can use Google's Structured Data Testing Tool to validate their schema markup and ensure its correct implementation.
20. Website’s Architecture
A well-structured, logically organized website is favored by Google.
Website architecture refers to the way a website is structured and organized, including the arrangement of its pages, navigation, and the relationships between different elements. A well-designed website architecture not only enhances the user experience but also plays a crucial role in search engine optimization (SEO) by making it easier for search engines to crawl, understand, and index the content.
A clear and logical hierarchy organizes the content of a website into categories and subcategories. This hierarchy is often represented in the navigation menu, making it easy for users and search engines to navigate through the site.
A clean and descriptive URL structure is important for both users and search engines. URLs should be readable, include relevant keywords, and reflect the content hierarchy. Avoiding complex URL parameters and using hyphens to separate words is a good practice.Example of a clean URL structure:
https://www.yourwebsite.com/category/subcategory/pageand for blog posts, a shorter one is even better. For Example:
https://www.yourwebsite.com/name-of-the-blog-postInternal linking involves connecting pages within the same website using hyperlinks. Well-planned internal linking helps distribute link equity, establishes content relationships, and guides users to relevant information. It also aids search engines in understanding the importance and context of different pages.
Including an XML sitemap helps search engines discover and index all the pages on a website. This is especially important for large websites with complex structures. In addition to an XML sitemap for search engines, an HTML sitemap can be created for users to navigate through the site easily.Mobile
With the increasing use of mobile devices, a website's architecture should be responsive, ensuring a seamless and user-friendly experience across different screen sizes. Google prioritizes mobile-first indexing, making mobile-friendly websites more favorable in search results.
Website architecture can impact page loading times. Optimizing images, utilizing browser caching, and minimizing unnecessary scripts contribute to faster page speeds, improving both user experience and search engine rankings.
Proper handling of 404 errors (page not found) is essential for user experience and SEO. Customized 404 pages can help users navigate back to relevant content, and regular checks for broken links are important for maintaining a healthy website.
Implementing canonical tags helps address duplicate content issues by indicating the preferred version of a page. This is particularly important for websites with similar or identical content on different URLs.
A well-structured website architecture enhances SEO by facilitating efficient crawling, providing a positive user experience, and signaling the importance and relevance of content to search engines. It contributes to better indexing, ranking, and overall visibility in search engine results.
User Interaction
21. Organic Click-Through Rate (CTR)
Google pays attention to how many clicks you're getting in comparison to your competitors.
Click-Through Rate (CTR) is a metric used in digital marketing and advertising to measure the effectiveness of an online campaign in terms of user engagement. It represents the percentage of people who clicked on a specific link or ad out of the total number of people who viewed it. The formula for calculating CTR is:
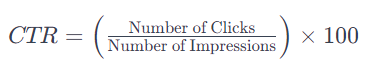
In the context of SEO, CTR is crucial because it indicates how well your search listings are performing in terms of attracting clicks from users. A higher CTR generally suggests that your page's title and meta description are compelling and relevant to users' search queries.
Crafting compelling and relevant title tags and meta descriptions can significantly impact your CTR. These elements are often displayed in search engine results and play a crucial role in attracting users to click on your link.
Including rich snippets, such as star ratings, product information, or other structured data, can make your search result stand out and potentially increase your CTR.
Pages that appear higher in search engine results pages (SERPs) often receive higher CTRs. Users tend to click on the first few results more frequently.
With the increasing use of mobile devices, optimizing for mobile search and ensuring that your snippets are mobile-friendly can impact your CTR.
Regularly monitor your CTR and test different elements, such as headlines and meta descriptions, to see what resonates best with your audience. Continuous optimization can improve your CTR over time.
22. Bounce Rate
If users are bouncing back to the SERPs after visiting your site, Google might downrank you.
Bounce rate refers to the percentage of visitors who navigate away from a website after viewing only one page. In other words, it measures the rate at which users "bounce" or leave a site without interacting further beyond the initial landing page. Bounce rate is an important metric used to assess the effectiveness of a website in retaining visitors and providing a satisfactory user experience.
Bounce rate is calculated by dividing the number of single-page sessions by the total number of sessions and then multiplying by 100 to get a percentage.
A high bounce rate may indicate that visitors are not finding the content, products, or information they expected, leading them to leave the site quickly. Conversely, a low bounce rate suggests that visitors are engaging with the content and exploring additional pages on the site.
Bounce rate should be interpreted in the context of the type of website and its goals. For certain pages, such as blog posts or news articles, a higher bounce rate might be acceptable if users find the information they need on the page. On e-commerce sites, a high bounce rate on product pages may be a concern.
It's often more informative to analyze bounce rates on a page-by-page basis. Understanding which pages have higher bounce rates can help identify areas for improvement in content, design, or user experience.
Several factors can contribute to bounce rate, including slow page load times, irrelevant content, poor navigation, confusing layouts, or an overall lack of engagement. Identifying and addressing these issues can help reduce bounce rates.
Some visitors may land on a page with a specific intent, such as finding a contact number or reading a specific piece of information. If they accomplish their goal on the landing page and exit, it doesn't necessarily indicate a negative user experience.
While bounce rate is not a direct ranking factor in search engine algorithms, user engagement metrics, including bounce rate, can indirectly influence SEO. Google aims to provide users with relevant and valuable content, and user behavior signals contribute to this assessment.
Monitoring and analyzing bounce rate alongside other user engagement metrics can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of a website's content and user experience, helping webmasters make informed decisions for optimization.
23. Dwell Time
The time a user spends on your site can also influence your ranking.
Dwell time refers to the amount of time that a user spends on a webpage after clicking on a search result but before returning to the search results. It is a user engagement metric that reflects how well the content on a page satisfies the user's intent and holds their attention.
Dwell time is calculated by measuring the time between a user clicking on a search result and returning to the search results. It is essentially the duration the user spends on the webpage.
Dwell time is related to other user engagement metrics such as bounce rate and time on page. However, it specifically focuses on the time a user spends on the page they initially clicked on from the search results.
Dwell time is closely tied to how well a webpage meets the user's intent. If the content is relevant, valuable, and satisfies the user's query, they are more likely to spend a longer time on the page.
Creating high-quality, engaging content is crucial for improving dwell time. Content that is informative, well-structured, and meets user expectations is more likely to keep users on the page.
The ideal dwell time can vary based on the type of content and user intent. For certain queries, a shorter dwell time might be acceptable if the user finds the information they need quickly. For more in-depth content, a longer dwell time may be expected.
While dwell time is not a direct ranking factor in search engine algorithms, it is considered as part of the overall user experience signals that search engines use to assess the relevance and quality of content. Pages with longer dwell times may be perceived as more valuable and may have a positive impact on SEO.
To improve dwell time, focus on providing relevant and engaging content, optimizing page load times, and ensuring a user-friendly experience. Internal linking to related content can also encourage users to explore more pages on the site.
Monitoring and analyzing dwell time, along with other user engagement metrics, can help website owners and SEO professionals understand how users interact with their content. This information can be used to refine content strategies and enhance the overall user experience.
24. Direct Traffic
Google considers the amount of direct traffic your site receives.
25. Repeat Visitors
Returning visitors can boost your Google ranking.
Domain Factors
26. Domain Age
Older domains may have a slight advantage over newer ones.
Domain age refers to the length of time a domain has been registered and active on the internet. It is one of the many factors that search engines consider when evaluating the authority and trustworthiness of a website. While domain age is just one of numerous factors, it can contribute to a website's overall credibility and influence its search engine rankings.
Search engines, particularly Google, may take into account the historical data associated with a domain, including its registration date, to assess the site's reliability. Older domains often have a longer track record, which search engines may interpret as a sign of stability and trustworthiness.
New domains may initially face challenges in SEO as they lack an established history. However, the impact of domain age diminishes over time as the website builds a track record of quality content, user engagement, and other positive signals.
If a domain is transferred from one owner to another, it retains its original registration date. However, search engines may consider changes in ownership as a factor in evaluating the domain's credibility.
While domain age is a consideration, search engines prioritize content quality, relevance, and user experience. A newer domain with exceptional content and positive user engagement can still rank well in search results.
The quality and quantity of backlinks pointing to a domain also influence its authority. Older domains may have had more time to accumulate backlinks, but the quality and relevance of those links are crucial.
Consistent and positive website performance over time, regardless of domain age, is key to maintaining or improving search rankings. Regularly updating content, addressing technical issues, and providing a positive user experience contribute to SEO success.
27. Keyword Appears in Top Level Domain
Having a keyword in your domain can be a relevancy signal.
28. Domain Registration Length
A longer registration length can indicate a legitimate website.
29. Country TLD Extension
Country-specific domain extensions (.us, .uk, .au) help rank for those particular countries.
30. Penalized WhoIs owner
In the context of SEO, the term "penalized WhoIs owner" generally refers to a situation where a website's owner or the registrant listed in the Whois database has faced penalties or sanctions from search engines, typically Google. The Whois database contains information about domain registrations, including details about the domain owner, contact information, and registration dates.
Search engines may impose penalties on websites or domain owners for various reasons, such as engaging in manipulative SEO practices, violating webmaster guidelines, or participating in activities that are deemed as spammy or deceptive.
The Whois database is a public record that provides information about domain registrations, including the name, contact details, and other information about the domain owner. This information is accessible to the public.
Some domain owners use privacy protection services to conceal their personal information in the Whois database. In such cases, the actual details of the domain owner may not be immediately visible to the public.
If a website with a penalized owner or domain faces SEO-related penalties, it may impact the site's rankings, visibility, and overall performance in search engine results. The penalties can extend to various aspects of SEO, such as manual actions or algorithmic penalties.
In cases where a website owner believes they have addressed the issues that led to penalties, they can submit a reconsideration request to the search engine. This involves explaining the corrective actions taken to comply with guidelines and requesting a review of the site's status.
In some cases, changing the ownership details in the Whois database may be considered as a strategy to distance the website from previous penalties. However, search engines are sophisticated in identifying ownership changes, and this alone may not necessarily lift penalties.
To avoid being a penalized WhoIs owner, it's crucial to adhere to search engine guidelines, engage in ethical SEO practices, and provide high-quality, user-centric content. Following best practices ensures a website's compliance with search engine guidelines and reduces the risk of penalties.
It's important to note that penalties are usually applied to websites based on their content, behavior, and adherence to search engine guidelines, rather than directly tied to the identity of the domain owner in the Whois database. However, transparency and ethical practices are fundamental in maintaining a positive online presence and avoiding potential penalties.
User, Usage, and Traffic/Query Data
31. Organic Traffic
Websites with more organic traffic are likely to rank higher.
Organic traffic refers to the visitors who come to a website through unpaid, natural search engine results. When users enter a query into a search engine like Google, the search engine returns a list of results based on its algorithms. Organic traffic consists of the users who click on these non-paid (organic) search results to visit a website.
Organic traffic is distinct from paid traffic, which involves users clicking on advertisements to visit a website. Organic search results are the listings that appear naturally based on relevance to the user's query and other SEO factors.
The visibility of a website in organic search results is influenced by its search engine rankings. Websites that appear higher in the search results are more likely to receive organic traffic, as users tend to click on the top results.
Organic traffic is often driven by the use of relevant keywords in a website's content. When users search for specific terms, search engines aim to deliver results that match those terms closely.
Search engine optimization (SEO) is crucial for improving organic traffic. By optimizing website content, meta tags, images, and other elements, webmasters can increase the likelihood of their site appearing in relevant search results.
Organic traffic is considered a long-term and sustainable strategy for attracting visitors to a website. While paid advertising can provide immediate results, organic traffic relies on the ongoing optimization of a site's content and its ability to rank well in search engines.
High-quality, relevant content is a key driver of organic traffic. Search engines aim to provide users with valuable and authoritative information, and websites with quality content are more likely to rank well.
Website owners can track and analyze organic traffic using tools like Google Analytics. This allows them to see which search queries users used to find their site, the pages they visited, and other important metrics.
For businesses targeting local audiences, local SEO strategies are essential to increase visibility in local search results. This can help attract organic traffic from users in specific geographic locations.
With the increasing use of mobile devices for internet browsing, optimizing for mobile is crucial for capturing organic traffic. Mobile-friendly websites are favored by search engines in their rankings.
Increasing organic traffic often involves a combination of technical SEO, on-page optimization, content creation, and link-building efforts. It is a fundamental aspect of digital marketing, and successful websites prioritize strategies to enhance their organic visibility and attract relevant visitors.
32. Traffic Consistency
Consistent traffic can signal that your site is relevant and updated.
33. Pogo-sticking
"Pogo-sticking" refers to the behavior where users click on a search result, visit a webpage, and then quickly return to the search results page to click on another result. This behavior may indicate that the initial webpage did not meet the user's expectations or provide the information they were seeking. Pogo-sticking can have implications for SEO and the ranking of pages in search engine results.
Pogo-sticking is seen as a negative signal regarding user satisfaction. If users consistently return to the search results after clicking on a page, it suggests that the content on the initial page did not fulfill their needs or expectations.
While bounce rate measures the percentage of single-page sessions where users leave without further interaction, pogo-sticking specifically refers to users bouncing back and forth between the search results and different pages. Pogo-sticking is a more dynamic indicator of user dissatisfaction.
Pogo-sticking underscores the importance of providing high-quality and relevant content. If a webpage fails to deliver the information or experience users are looking for, they are more likely to pogo-stick to other search results.
Search engines, such as Google, aim to provide users with the best possible results for their queries. Pogo-sticking can be interpreted as a signal that a particular webpage may not be the most relevant or useful for a given search query. Over time, this could impact the ranking of that page in search results.
Pogo-sticking is related to CTR. A low CTR (few clicks relative to impressions) may lead to pogo-sticking behavior if users find the content unsatisfactory. Improving meta titles, descriptions, and overall content relevance can positively impact CTR and reduce pogo-sticking.
To minimize pogo-sticking, website owners and SEO professionals should focus on optimizing the user experience. This includes ensuring that content is relevant, well-organized, and easy to navigate.
With the increasing use of mobile devices, ensuring that a website is mobile-friendly is crucial for preventing pogo-sticking. Mobile users expect fast-loading and responsive pages, and a poor mobile experience may lead to quick exits and pogo-sticking.
Webmasters can use analytics tools to monitor user behavior on their websites. Tracking bounce rates, time-on-page metrics, and identifying pages with high pogo-sticking rates can provide insights into areas that need improvement.
Addressing pogo-sticking involves a holistic approach to website optimization, focusing on content quality, relevance, user experience, and technical aspects. By meeting user expectations and delivering valuable content, websites can reduce pogo-sticking, enhance user satisfaction, and positively impact their SEO performance over time.
34. Number of comments
The number of comments on a webpage can have both direct and indirect effects on SEO (Search Engine Optimization). Here are some ways in which the number of comments may impact SEO:
The number of comments on a page is often seen as an indicator of user engagement. A higher number of comments may suggest that the content is resonating with the audience and generating discussion. Search engines often consider user engagement as a positive signal when ranking pages.
Comments contribute to the freshness of content. When users leave comments, it indicates ongoing interest and activity around the content. Search engines, like Google, often value fresh and updated content, and regularly commented-on pages may be seen as more relevant.
Comments can introduce additional keywords and phrases related to the content of the page. This user-generated content can enhance the overall keyword relevance of the page, potentially broadening its search visibility for related queries.
If users spend time reading the content and engaging in the comments section, it can contribute to increased dwell time. Dwell time, the amount of time users spend on a page before returning to search results, is considered a positive user experience signal.
A high number of comments can serve as social proof, indicating that the content is valuable and has sparked interest. This social validation can influence users and may indirectly contribute to increased click-through rates from search results.
Websites with active and engaged communities, often reflected in the number of comments, may gain a reputation for being authoritative and trustworthy. Search engines may consider such signals when evaluating the overall authority of a site.
Search engines may index and consider the content of user comments. This can contribute to a broader range of relevant keywords associated with the page. However, it's important to note that not all user-generated content, especially spam or low-quality comments, may be beneficial.
User comments may introduce long-tail keywords and variations that users commonly use in natural language. This can enhance the page's semantic relevance and improve its chances of ranking for a variety of search queries.
It's important to highlight that the impact of comments on SEO can vary based on the quality and relevance of the comments. Spammy or irrelevant comments may have a negative impact, while thoughtful and engaging comments can enhance the overall user experience and SEO performance of a page.
Website owners and content creators should actively moderate comments, encourage meaningful discussions, and foster a positive community to maximize the potential benefits of user comments for SEO. Additionally, providing valuable and shareable content is key to encouraging user engagement and generating meaningful comments.
35. Blocked Sites
Google may devalue sites that users block in their Google settings.
Special Algorithm Rules
36. Query Deserves Freshness (QDF)
Google gives newer pages a boost for certain searches.
Query Deserves Freshness (QDF) is a concept in SEO that reflects search engines' tendency to prioritize fresh and up-to-date content for certain search queries. The idea behind QDF is that for some topics or events, users are more likely to be interested in the latest information. Therefore, search engines may boost the rankings of newer content to meet the user's expectation for freshness.
QDF is driven by the temporal relevance of content. Some search queries are more time-sensitive, and users are likely seeking the most recent information available.
QDF is particularly relevant for news-related queries, trending topics, and events. Search engines aim to provide users with the latest and most relevant news articles or information when they are searching for current events.
Search engines, like Google, use algorithms to dynamically adjust rankings for certain queries based on the expectation of freshness. This adjustment is more noticeable for queries where recent updates or developments are crucial.
Google has implemented specific updates to its algorithms to address the freshness of content. The "Freshness Update," introduced in 2011, was designed to improve the visibility of recently updated or published content for specific queries.
While QDF is important for time-sensitive content, it doesn't apply to evergreen content—information that remains relevant over time. Evergreen content may not be subject to the same freshness considerations as time-sensitive content.
Understanding user intent is critical in the context of QDF. For queries where users are likely seeking the latest information, search engines aim to deliver results that align with that intent.
Regularly updating content can be a strategy to align with QDF, especially for websites that focus on topics where freshness is a significant factor. Updating articles, blog posts, or news stories helps signal to search engines that the content is current.
QDF can lead to fluctuations in rankings, especially for content that quickly becomes outdated or irrelevant. Newer content may experience a temporary boost in rankings as search engines prioritize freshness.
It's important for content creators and website owners to be aware of QDF, especially in industries or niches where timely information is crucial. Staying informed about industry trends, events, and news can help ensure that the content remains relevant and competitive in search engine rankings.
37. User Search History
Google may display different results based on the user's search history.
38. Transactional Searches
"Transactional searches" refer to a type of search query where users are actively seeking to make a transaction or take a specific action. These searches are characterized by a clear intent to purchase a product, subscribe to a service, or complete a specific online transaction. While transactional searches themselves are not a direct Google ranking factor, they are part of the broader context that search engines consider when delivering search results.
Transactional searches indicate a high level of user intent to perform an action, such as making a purchase. Understanding user intent is crucial for search engines to provide relevant and satisfactory results.
Many transactional searches are related to e-commerce and commercial activities. For example, users might search for "buy iPhone online" or "best laptop deals." Google recognizes commercial intent and strives to present results that align with users' shopping goals.
Transactional queries often trigger a mix of paid and organic results. Paid advertisements from businesses looking to capture transactional intent may appear prominently in search results, alongside organic listings that are optimized for the same intent.
Google may enhance search results for transactional queries with rich snippets, including product listings, prices, and reviews. Websites that provide structured data to facilitate this information may have a competitive advantage in transactional search results.
For transactional searches with a local intent, such as "near me" queries, Google prioritizes local businesses and may display map packs, local listings, and directions to physical stores.
While not a direct ranking factor, the user experience on landing pages that cater to transactional searches is essential. Pages that load quickly, offer a seamless checkout process, and provide relevant information have a higher likelihood of satisfying user intent.
Given the prevalence of mobile searches, transactional queries often occur on mobile devices. Mobile-friendly websites and those with a smooth mobile checkout experience are more likely to perform well for transactional searches.
Trust is crucial for users engaging in transactional searches. Websites with secure payment methods, clear privacy policies, and trust signals may be preferred by both users and search engines.
While not directly related to rankings, optimizing for transactional searches often involves focusing on conversion rate optimization. Websites that effectively convert visitors into customers may benefit from improved organic visibility over time.
It's important for businesses to understand the specific intent behind transactional searches relevant to their products or services. Optimizing content, product pages, and the overall user experience for transactional intent can contribute to a positive online presence and potentially impact rankings indirectly. Additionally, businesses should stay informed about Google's guidelines and best practices for e-commerce and commercial websites.
39. Geo-Targeting
Location impacts SERP rankings.
40. Safe Search
Offensive or inappropriate content is demoted in SERPs.
Safe Search is a feature implemented by search engines, most notably by Google, to filter explicit or inappropriate content from search results. The primary purpose of Safe Search is to provide a safer and more family-friendly browsing experience by blocking or restricting access to content that may be considered explicit, offensive, or inappropriate.
Safe Search filters search results to exclude explicit content, including adult content, violence, and other types of content that may be unsuitable for certain audiences.
Search engines typically allow users to enable or disable Safe Search settings based on their preferences. Users, especially parents, can configure these settings to ensure a more controlled and secure browsing experience for themselves and others.
The filters used in Safe Search are algorithmically designed to identify and filter out content that violates safe browsing guidelines. The algorithms consider factors such as keywords, images, and website characteristics to determine the appropriateness of content.
Safe Search is often enforced on school networks, public places, and other environments where content filtering is necessary to comply with safety and regulatory standards. Educational institutions and organizations may use Safe Search to create a safer online environment for students or employees.
For website owners and creators of online content, ensuring compliance with Safe Search guidelines is essential to maintain a broader audience. Websites featuring explicit content may be filtered out of search results when Safe Search is enabled, potentially impacting their visibility.
Google, one of the leading search engines, has its SafeSearch feature. Users can access SafeSearch settings in their Google accounts to customize the level of filtering applied to their search results.
Webmasters and content creators should be mindful of Safe Search guidelines to avoid unintentional filtering of their content. This includes using appropriate metadata, tags, and descriptions to accurately represent the content on their pages.
Google provides a Safe Search API that developers can use to incorporate Safe Search features into their applications or websites, ensuring a more controlled environment for users.
Ensuring that content aligns with Safe Search guidelines is important for website owners and creators, especially if their target audience includes users who may have Safe Search enabled. Adhering to community guidelines and creating content that is suitable for a wide audience contributes to a positive online experience and helps maintain a good reputation in search results.
Social Signals
41. Number of Tweets
The number of tweets a page has can influence its ranking in Google.
42. Authority of Twitter Users Accounts
Tweets coming from high authority accounts could increase a page's ranking.
43. Number of Facebook Likes and Shares
These can influence a page's position in Google.
44. Pinterest Pins
Pinterest is popular with Google, high number of pins can boost ranking.
45. Votes on Social Sharing Sites
Votes from sites like Reddit, StumbleUpon and Digg can help ranking.
Brand Signals
46. Brand Name Anchor Text
Branded anchor text can help boost your site's ranking.
Brand name anchor text refers to the use of a brand's name as the clickable text (anchor text) in hyperlinks pointing to a particular website or webpage. It is one of the types of anchor text used in backlinks and is considered a natural and brand-focused approach to link building.
Brand name anchor text is considered a natural way of linking because it typically reflects how users naturally link to a website when mentioning its brand or name.
The use of brand name anchor text provides strong branding signals to search engines. It helps search engines understand the association between the anchor text and the brand, contributing to the overall authority and identity of the brand online.
A healthy backlink profile often includes a variety of anchor text types, including brand name, exact match, partial match, and generic anchor text. This diversity is considered more organic and less likely to raise flags with search engines.
Brand name anchor text is especially valuable for building brand authority in search engine algorithms. The more authoritative and trustworthy a brand is perceived, the more likely it is to rank well in search results.
Monitoring brand mentions across the web and ensuring that brand names are used as anchor text when appropriate is a proactive approach to building brand visibility and authority.
It's important to note that while brand name anchor text is valuable, a balanced and varied anchor text profile is essential for a natural and organic backlink profile. Overemphasis on any single type of anchor text, including brand name, can potentially raise concerns with search engines. A holistic approach to link building that prioritizes the brand's identity and authority is recommended for long-term SEO success.
47. Branded Searches
People searching for your site on Google (brand + keyword) can boost your ranking.
48. Site Has Facebook Page and Likes
Brands that have a lot of likes on their Facebook page may rank higher.
49. Site Has Twitter Profile with Followers
Having a popular Twitter account can improve your ranking.
50. Unlinked Brand Mentions
Brand mentions may occur without direct hyperlinks, but they still contribute to your online presence. Google perceives non-hyperlinked brand mentions as significant signals for your brand.
Conclusion
Understanding and implementing these 50 ranking factors can significantly improve your site's visibility on Google. However, remember that SEO is a long-term strategy, and changes won't happen overnight. Stay consistent, patient, and always prioritize providing value to your audience above all else.

